oxygen delivery devices and flow rates australia
Give oxygen therapy in a way which prevents excessive CO 2 accumulation - ie. It varies from 0 15L per minute.
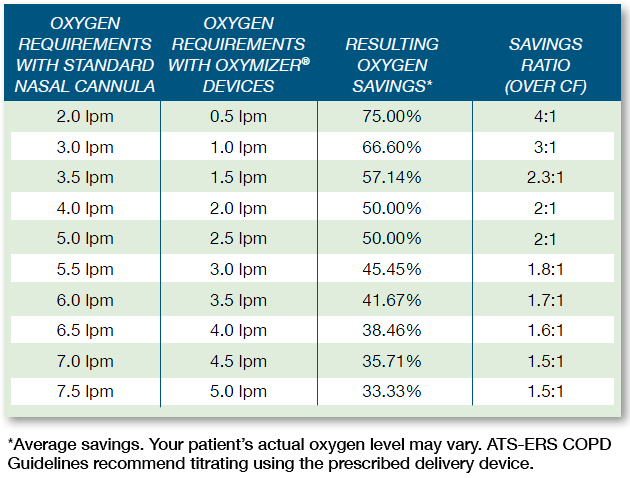
Chad Oxymizer Disposable Oxygen Conserver Oxygen Reservoir Drive Medical O 224 P 224 Vitality Medical
2 to 15 Lmin.
. Venturi masks are high flow delivery devices. The flow rate can be set on the wall tap. Very commonly used among the Oxygen Delivery Devices in wards.
Can delivery precise and dependable FiO2. Values at various flow rates. A 28 valve will have a smaller hole than a 40 valve and so on.
Of the commonly available devices promoted for O₂ delivery to injured divers similar PtcO₂ and nasopharyngeal F I O₂ values were obtained with the three devices tested. Dropping the oxygen flow rate closer to 10 Lmin-1 has been suggested as a compromise but the. Low flow device Most common device used for mild hypoxia Can be set between 1 and 6 LPM 24 to 40 FiO2 FiO2 increases approximately 4 with each liter of O2 KorupoluR GJ Needham DMContemporary CriticalCare.
200969111 Bailey P Thomsen GE Spuhler VJ et alCrit Care MedJan2007351139145. 25 FiO 2 at 15 Lmin 90 FiO 2 at 15 Lmin FiO 2 can be adjusted to between 25 and 90 by changing the flow rate Conclusion OxyMask effectively delivered a wide range of FiO 2 values through simple adjustments to the flow rate. Also known as Mary Carterall mask.
This delivers to the patient a flow rate of 45 liters per minute and an oxygen concentration of 35 percent. If oximetry is not available or reliable oxygen saturations cannot be determined and hypoxaemia is suspected oxygen can be delivered at. For example the recommended flow rate for a 35 of venturi valve is 8 liters per minute.
The nasal cannula is a device that has two prongs that are placed in the patients nostrils and deliver oxygen at flow rates of 1 to 6 liters per minute. Nasal Cannula 1-6 litersminute 25-50 Humidifier recommended for all flow rates 4 litersminute High Flow Nasal Cannula 1-15 litersminute 25-50. Only goes up to 60 FIo2 so not for patients who have significantly high oxygen demands bulky.
However when breathing with the NRB an O 2 flow rate of 15 Lmin-1 is required to reach these levels. When delivering oxygen by wafting the highest oxygen concentrations are achieved when positioning tubing 5-15 cm in front of the face or positioning tubing or a paediatric non-rebreather mask 5-10 cm below. 5L 40 6L 44.
6 rows Device. 1-2 Lmin via nasal cannulae or 2-4 Lmin via 24 or 28 Venturi mask in patients with acute exacerbations of COPD or conditions known to. They include Nasal cannulae.
They have valves which deliver a fixed concentration of oxygen eg. Domiciliary oxygen a nd equipment may be provided for adults with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Adapters deliver set amounts of FiO2 at 24 to 60.
The recommended initial oxygen flow rate for open-circuit systems employing a non-rebreather mask has long been 15 Lmin-1. Domiciliary oxygen and equipment may be provided for adults without. OxyMask is an all-in-one replacement for other mask types which could save time and reduce trips to the.
Based on transcutaneous oximetry values of the commonly available emergency O₂ delivery devices the NRB at 15 Lmin ¹ is the device and flow rate that deliver the most O₂ to body tissues and therefore should be considered as a first-line pre-hospital treatment in divers with suspected decompression illness. MORS with an oronasal or intraoral mask demand valve with an intraoral mask and NRB at a flow rate of 15 Lmin¹. These low flow Oxygen Delivery Devices are variable performance devices ie their performance is effected by changes in patients tidal volume and respiratory rate.
These devices deliver a variable inspired oxygen concentration to the patient which depends on the PIFR. Ensure adequate clearance of secretions and limit the adverse events of hypothermia and insensible water loss by use of optimal humidification dependent on mode of oxygen. Delivery devices work with different flow rates.
Peak nasopharyngeal F I O 2 was highest with the NRB with a flow rate of 15 Lmin-1 Table 3 though 10-min P tc O 2 values were similar for each device. When tubing was used below the face flow rates between 6 and 8 Lmin produced somewhat higher concentrations than 15 Lmin 5 cm. Demonstrated oxygen desaturation on oximetry or arterial blood gases at rest on exercise or nocturnal with SaO2 less than 90 or PaO2 less than 60mmHg is required.
Flow rate 1-4Lmin 4L will dry the nose 2L is more comfortable. 1 to 6 liters. We come to you.
2435 FiO2 at a flow of 14. Depending on a patients inspiratory effort tidal volume speed of inspiration and respiratory rate the PIFR can often exceed the flow rate at which oxygen or an oxygenair mixture is supplied by the device meaning that at the time of PIFR. Different oxygen flow rates result in a highly variable and unpredictable FiO 2 Rebreathing of CO 2 can occur with O 2 flow rates of less than 2 L O 2 lmin or if minute ventilation is very high 4 Lmin of oxygen flow delivers an FiO 2 of about 03504 providing there is.
The percentage of oxygen inspired depends on the flow rate and the delivery device. Given typical supply limitations there is a natural interest in reducing the flow rate to extend oxygen delivery duration. Each valve is colour coded Figure 3 although newer valves can be set at the desired FiO2 in a single unit.
Ad Oxygen Therapy Specialists Australia Wide. Selection of the appropriate flow rate and delivery device. Oxygen Delivery Devices Delivery Device Minimum to Maximum Liter Flow Range Adults Approximate O2 Delivered Notes RT assistance recommended for liter flows of 6 litersminute or more.
Per minute will deliver approximately 24 to 44 percent of oxygen to the patient. Reduce the work of breathing. Increasing the flow rate to 10 liters per minute increases the total flow to the patient but the oxygen concentration delivered remains at 35 percent.

Transtracheal Catheter Image Courtesy Www Airwayeduca Download Scientific Diagram
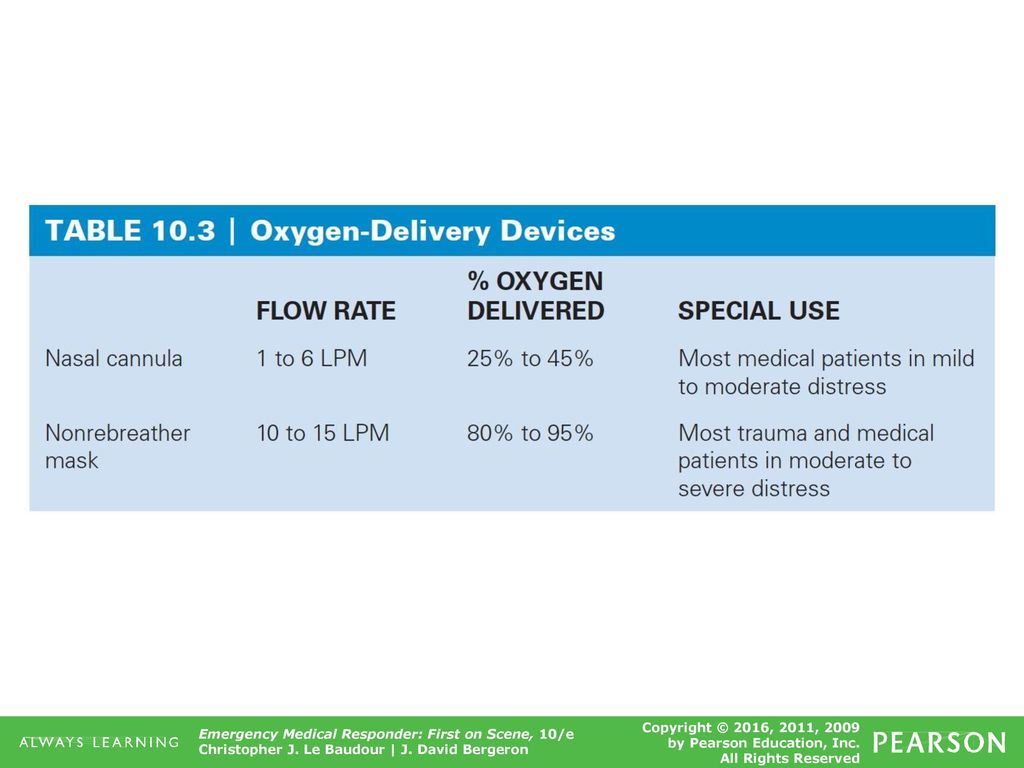
10 Principles Of Oxygen Therapy Ppt Download

Transtracheal Catheter Image Courtesy Www Airwayeduca Download Scientific Diagram

High Flow Nasal Oxygen Therapy In Patients After Cardiac Surgery Semantic Scholar
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Initial Or Starting Flows Of High Flow Nasal Cannula In A Pediatric Download Table

Buy Hospital Bed In 2021 Hospital Hospital Bed Best Hospitals

Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Equation For Oxygen Delivery Download Scientific Diagram
High Flow Oxygen Therapy Devices Market By Product Application End User Region For 2021 2031 Global Sales Analysis And Opportunity 2031 Fmi
